 |
Software Quality Assurance
|
|
 |
Software Quality Assurance
|
|
The following section describes all tests that are carried out before delivery, so-called Release Tests, see Deployment. The following types of tests are distinguished:
Further information:
The following table gives an overview about the current release tests related to the test scope.
| Test Scope | How? | What? | Current Test Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard compliance Is the execution of OTX procedures standard compliant? | OTX Tests | Runtime | 95% |
| Integrability How smoothly can new versions be integrated into real systems? | API Tests, Integration Tests, Use-Case Tests | APIs | 90% |
| Runtime behavior Are the requirements regarding performance, memory consumption and parallelism met? | Integration Tests, Use-Case Tests | Runtime | 70% |
| Reality Does the software behave as expected for general and specific use cases? | Use-Case Tests | Runtime | 10% |
| FOSS Are all legal requirements for the use of open source components met? | FOSS Test | Runtime, OTF | 100% |
To understand the tests, the rough structure of the software is shown in the picture below. From a testing perspective, the software consists of the following components, which are tested in different ways. The ways are described below.
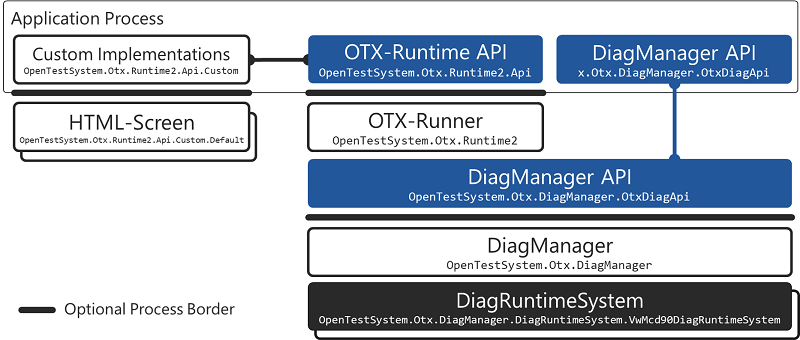
The following image shows the various areas for test security of the OTX runtime API. The OTX Tests are test procedures written in OTX with the UnitTest extension. They contain Unit Tests to ensure the standard conformity of single components like actions, terms, branches, handler end nodes, etc. as well as simple Integration Tests for the combination of multiple components like ODX browsing, running diagnostic services or jobs, handling large lists or maps, reading and writing large XML files, multithreading etc. The user can also define special Integration Tests, so-called Use-Case Tests. Use Case tests represent a specific, real-world application, e.g. FAP-Reading, ECU-Flashing.
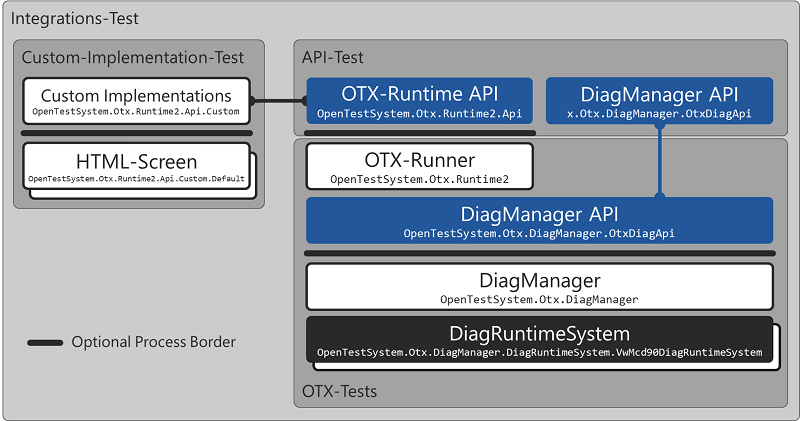
The API Tests test all public properties, methods, events and interfaces (for the custom implementations) of all APIs of the OTX Runtime and the DiagManager for C++, DotNet and Java. The Custom Implementation Tests without Default Implementation secure the expected runtime behavior of the supplied default custom implementations such as HTML screen or assembly screen.
In the OTX test, test cases are written in OTX with the OTX-UnitTest extension inside the Open Test Framework. This tests the standard conformity of the OTX runtime. The test cases are created within the OTF as OTX-UnitTests and executed and logged in the OTF's test explorer, see code example below.
Note: The diagnostic communication is simulated, see Environment Simulation.
The following table (as of 12/2024) show the number of test cases:
| Test Object | Number |
|---|---|
| OTX-Tests with DiagCom | 4.363 |
| OTX-Tests without DiagCom | 5.306 |
| Total | 9.669 |
While unit tests test individual components (units), integration tests test the practical interaction of several components. The integration tests are intended to ensure the expected behavior under conditions that are as realistic as possible with regard to correct function and runtime requirements.
Various integration tests are implemented, e.g. sending and receiving diagnostic services as quickly and as parallel as possible.
Note: The integration tests are part of the OTX Tests and are implemented there.
Use case tests are Environment Simulation only implemented for an actual use case. The use case can be general or user-specific. The aim is to run scenarios that are as real as possible under real conditions, automatically. The following use case scenarios should be tested:
Note: The use-case tests are part of the OTX Tests and are implemented there.
API tests are regression tests of all interfaces of the OTX Runtime API and the DiagMaster API, see table below, to ensure that changes to the software do not cause unintended changes (bugs or regressions) to the API, see code example. API tests are executed and logged for all public properties, methods, events and interfaces of all delivered APIs.
The following table (as of 12/2024) show the number of test cases:
| Test Object | Lang. | IPC | Win | Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OTX-Runtime Api | Cpp | Pipe | Win32 | 783 |
| OTX-Runtime Api | Cpp | Pipe | Win64 | 783 |
| OTX-Runtime Api | Cpp | Raw | Win32 | 783 |
| OTX-Runtime Api | Cpp | Raw | Win64 | 783 |
| OTX-Runtime Api | Cpp | Socket | Win32 | 783 |
| OTX-Runtime Api | Cpp | Socket | Win64 | 783 |
| OTX-Runtime Api | DotNet | Pipe | Win32 | 773 |
| OTX-Runtime Api | DotNet | Pipe | Win64 | 773 |
| OTX-Runtime Api | DotNet | Socket | Win32 | 773 |
| OTX-Runtime Api | DotNet | Socket | Win64 | 773 |
| OTX-Runtime Api | Java | Pipe | Win32 | 773 |
| OTX-Runtime Api | Java | Pipe | Win64 | 773 |
| OTX-Runtime Api | Java | Socket | Win32 | 773 |
| OTX-Runtime Api | Java | Socket | Win64 | 773 |
| DiagManager Api | Cpp | - | Win32 | 1.537 |
| DiagManager Api | Cpp | - | Win64 | 1.537 |
| DiagManager Api | DotNet | - | Win32 | 1.386 |
| DiagManager Api | DotNet | - | Win64 | 1.386 |
| DiagManager Api | Java | - | Win64 | 1.468 |
| DiagManager Api | Java | - | Win32 | 1.468 |
| DiagManager CommandProcessor | Cpp | - | Win32 | 351 |
| DiagManager CommandProcessor | Cpp | - | Win64 | 351 |
| OTX-Runner | Cpp | - | Win32 | 401 |
| OTX-Runner | Cpp | - | Win64 | 401 |
| Total | 21.168 |
Alle Custom-Interfaces werden über die OTX-Unit-Test Extension getestet. Dabei werden die mitgelieferten Default-Implementierungen nicht getestet. Für jede Custom Implementation werden Testfälle mit der OTX-Unit-Test Extension geschrieben, siehe CallbackProcedure. Dies betrifft die folgenden Implementierungen:
Note: The custom implementation tests are part of the OTX Tests and are implemented there.
Alle Custom-Interfaces, die eigenständige Default-Implementierungen besitzen, z.B. DefaultCustomScreenImplementation werden mit der OTX-Unit-Test Extension über spezielle Implementierungen getestet, beispielsweise eine HTML-Screen-Implementierung, der definierte Werte zurückgibt.
Note: The custom implementation tests are part of the OTX Tests and are implemented there.
For the tests, the diagnostic communication is simulated at the D-PDU API level. This guarantees consistent, hardware-independent test results. The PDU simulation supplied in the OTF, including the PduSimulation extension, is used as the PDU simulation. This allows all relevant aspects of diagnostic communication to be simulated:
Note: The PDU simulation can currently only run under Windows. Therefore, no diagnostic-relevant tests can be carried out under Linux.
In accordance with the legal rules for the use of open source components, the use of FOSS components is checked and documented via review and audit, see user documentation. Only the changes are ever considered.
Note: In the past, a tool-supported FOSS check via Black Duck has already carried out.
Note: During the manual FOSS check, only the changes to the previous version are ever considered.
| Test Object | Report Example |
|---|---|
| OTX Unit Test Report for all TestCases without diagnostic communication | OTXUnitTestReport_7.62.48298.51676_NoDiagnosticTestCases.xml |
| OTX Unit Test Report for all TestCases with diagnostic communication | OTXUnitTestReport_7.62.48298.51676_DiagnosticTestCases.xml |
| OTX-Runtime API Unit Test Report for CPP and Socket at Win64 | OpenTestSystem.Otx.Runtime2.Api.Cpp.UnitTest.Socket.Win64.Report.7.62.48298.51676.xml |
| DiagManager API Unit Test Report for CPP | TestDiagManagerApi_Cpp_Win64.xml |
| DiagManager Command Processor Unit Test Report | TestCommandProcessor.Win64.Report.xml |
| OTF Unit Test Report for the model namespace | OpenTestSystem.Otf.Model.Tests.Report.7.62.48298.51676.xml |
| Virus Check Report | VirusTotal_Report_Win32_7.62.48298.51676.xml |